The *updated* pathway to:
Virtual Power Plants Commercial Liftoff
Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) are solutions that can be deployed at scale in a short timeframe to maximize the use and value of existing grid infrastructure, minimize costs to ratepayers, and ensure a resilient, reliable, and secure grid for all Americans.
Since the publication of the 2023 Liftoff Report, the near-term pressures on the U.S. electric grid have only intensified:
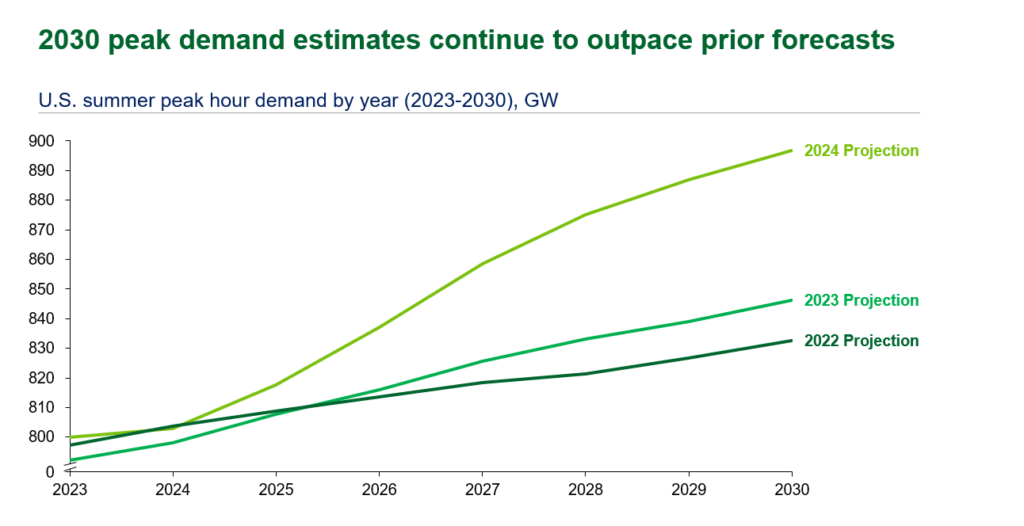
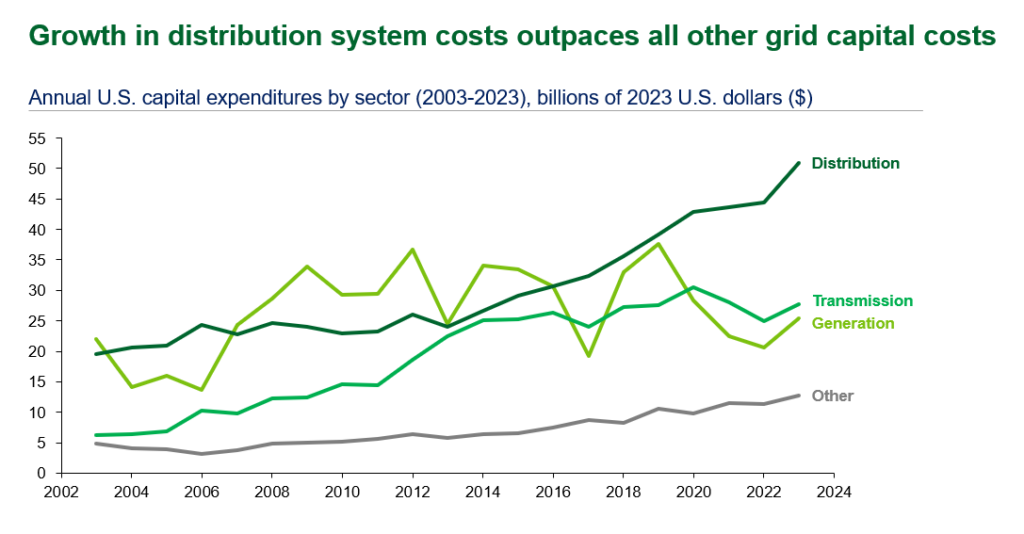
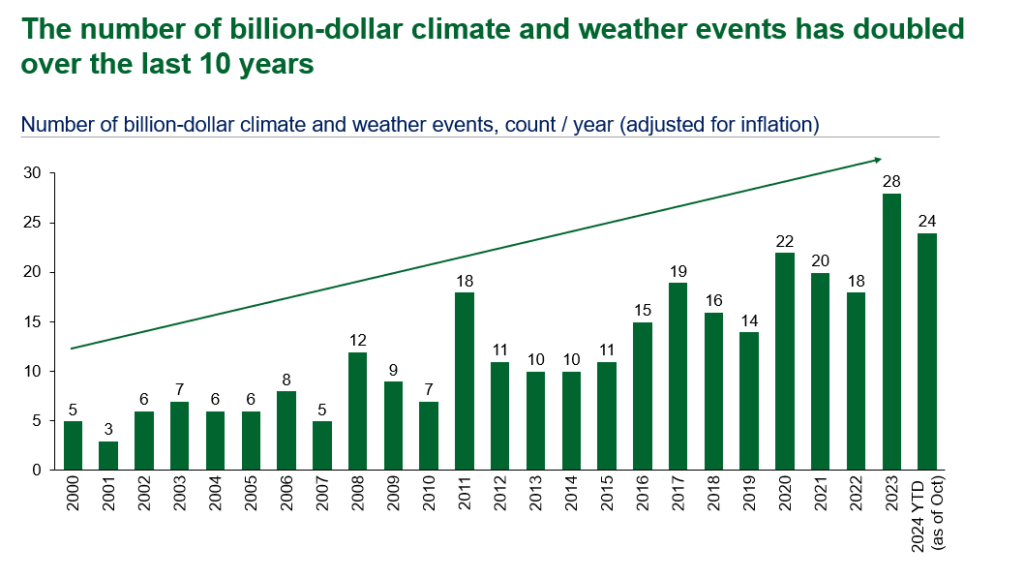
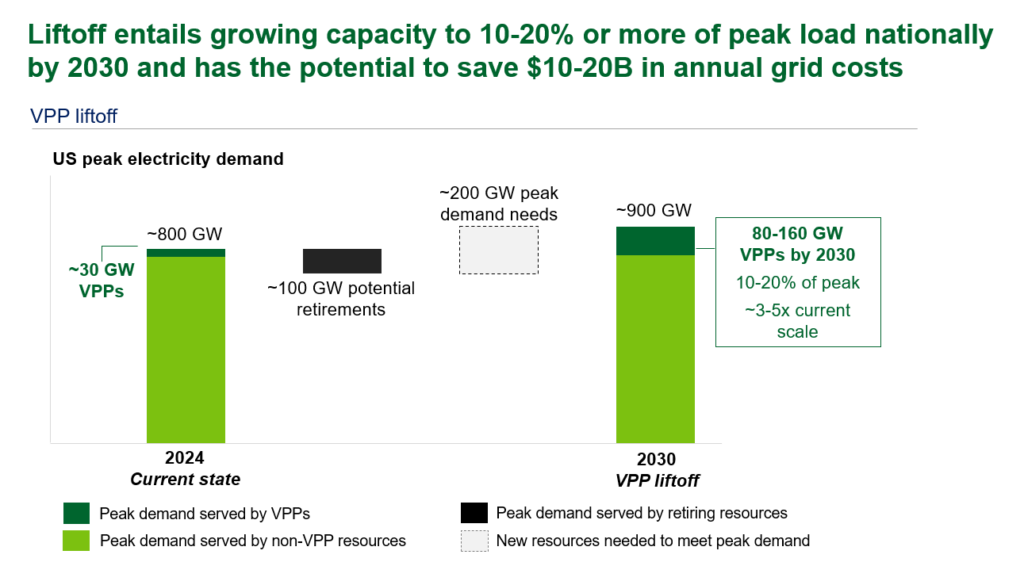
VPPs are among the critical solutions to meet the pressing challenges the grid faces today and in the near-term. Deploying 80-160 GW of VPPs (enough to serve 10-20% of peak load) by 2030 could support rapid load growth while reducing overall grid costs. Although VPP scale has grown to 33 GW across North America, the pace of deployment still needs to accelerate to achieve liftoff.
What are Virtual Power Plants (VPPs)?
VPPs are aggregations of distributed energy resources (DERs) such as smart appliances, rooftop solar with batteries, EVs and chargers, and commercial and industrial loads that can balance electricity demand and supply and provide grid services like a traditional power plant.
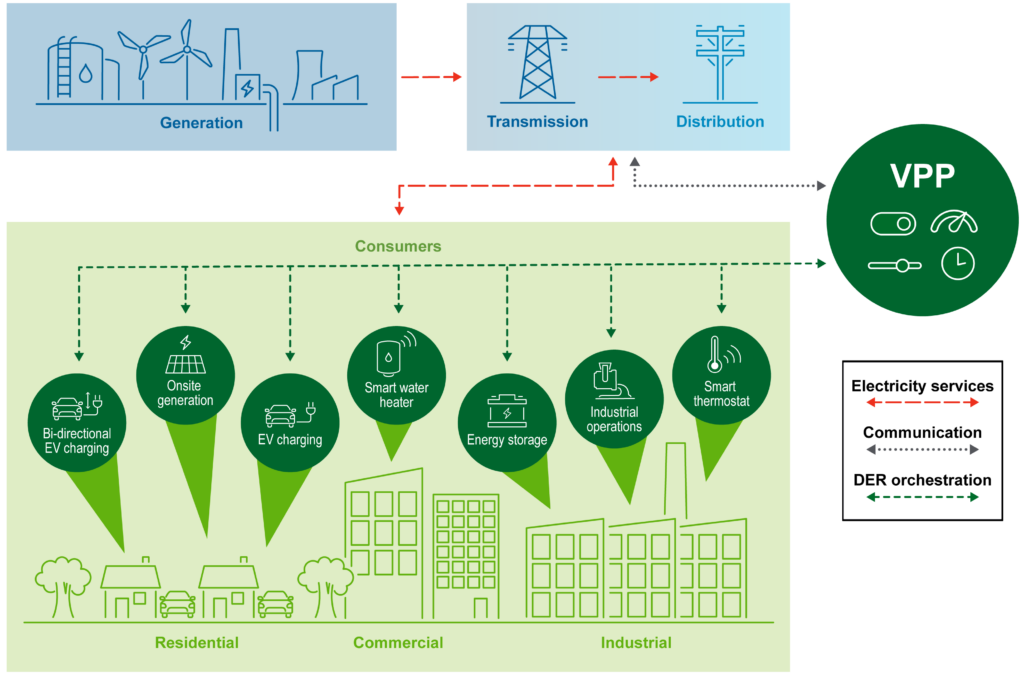
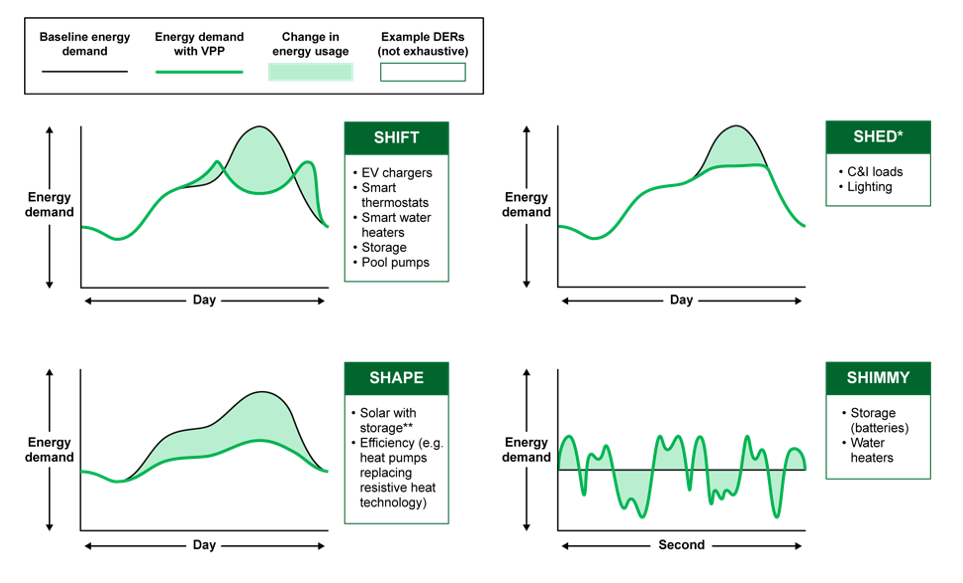
There are many kinds of VPPs that function in different ways to meet the needs of the local or regional grid. Functions in use today include: Supplying homes with energy from on-site solar-plus-storage systems during peak hours when bulk power generation is scarce; Shifting the timing of EV charging to avoid overloading local distribution system equipment; Charging distributed batteries (increasing demand) when electricity is abundant to reduce curtailment, for example, of utility-scale solar.
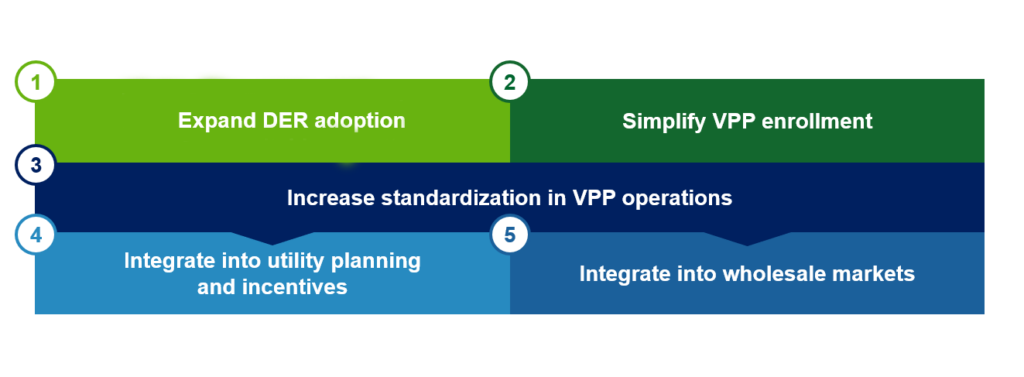
The pathway to commercial liftoff for VPPs requires progress on five imperatives:
The VPP Liftoff Update includes over 75 examples of actions that various stakeholders are implementing today as well as over 60 complementary programs and resources that the DOE and its collaborators have established to accelerate deployment.
Example actions from the last year supporting progress towards VPP liftoff:
Expand DER adoption
Simplify VPP enrollment
Increase standardization in VPP operations
Integrate into utility planning and incentives
Integrate into wholesale markets
Want to learn more?
The U.S. Department of Energy, in partnership with other federal, state, and local agencies, has tools to address challenges to commercial liftoff and is committed to partnering with the private sector to lead the commercialization of affordable energy resources while proactively responding to the nation’s growing energy demand.



